SEO
Everything About Google Search Console in 2020 and later
What is the Search Console?
The Search Console is a free analysis tool offered by Google. This means that webmasters have a very fine tool at hand - because the GSC helps you to keep an eye on the current status quo of your website on Google and provides valuable information on where it still has problems. Among other things, the Search Console provides information about the performance of your current URLs, any technical errors, and recommendations for improvements. The best: This data comes directly from Google and you can use it to communicate with the search engine. You can use the GSC to check whether Google interprets your pages as you would like them to be. As this is not always the case, you should definitely use this tool!
Setting it up: Domain property vs. URL prefix
For over a year now there has been the option not only of entering individual URLs for domains or directories, but also properties for complete domains. If you create a new property in the GSC, you will be offered these two options - the information on the individual property types is included:
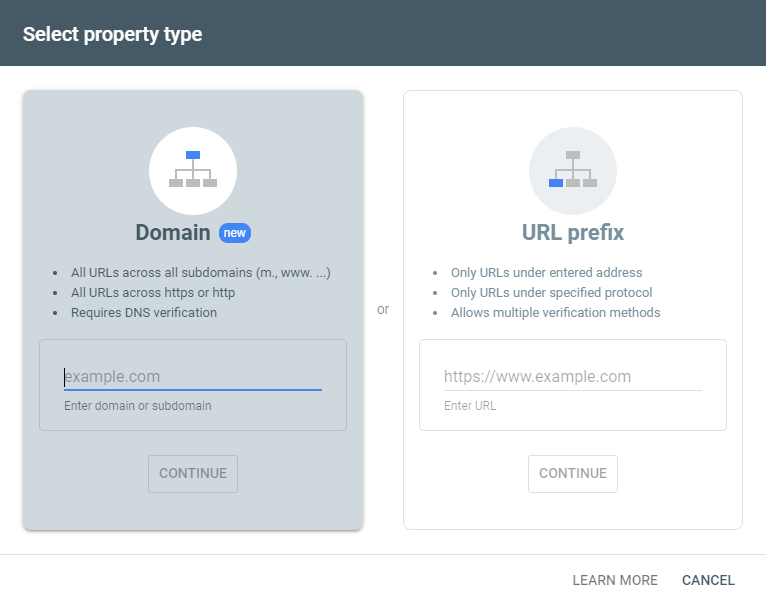
The domain property has the advantage that you can see and check all possible domain and protocol variants - with or without https with a property. You only have to confirm your domain once as a DNS entry with your domain provider. For example, if you have subdomains or have recently converted your website to https, you can view their performance bundled within the property. You may also discover completely new subdomains that generate impressions and/or clicks - whether wanted or unwanted ? In addition, you don't always have to switch between the individual properties but have an overview of all (sub) domains. A detailed overview of the different types, including instructions on the setting is provided by Google here.
It is important to note at this point that the previous reports and tools for domain properties are currently no longer available, as there is no complete replacement for them in the new Search Console. These include international orientation, crawling statistics, news, URL parameters, and web tools. In addition, you have to be a little careful with the assignment rights if you only want to grant people access to certain URLs, directories, or subdomains. You should continue to set up the individual URL prefix properties for this.
Which keywords does my page rank for?
Would you like to know which search terms users use to get to your website? Then the Google Search Console is your tool. Because you can easily find this out in the performance report, which can be controlled on the left using the "Overview" navigation. By default, the data from the last three months is always displayed here. With this overview of search queries, you already get a rough idea of what your website is ranked in in the Google search engine. In addition, you will find out which keywords your website is seen by users (= receives impressions), how many clicks actually result from it, a click-through rate (CTR) based on it, and the average position of the keyword.
The default settings are such that your search queries are already displayed according to clicks (= visits generated using this keyword):
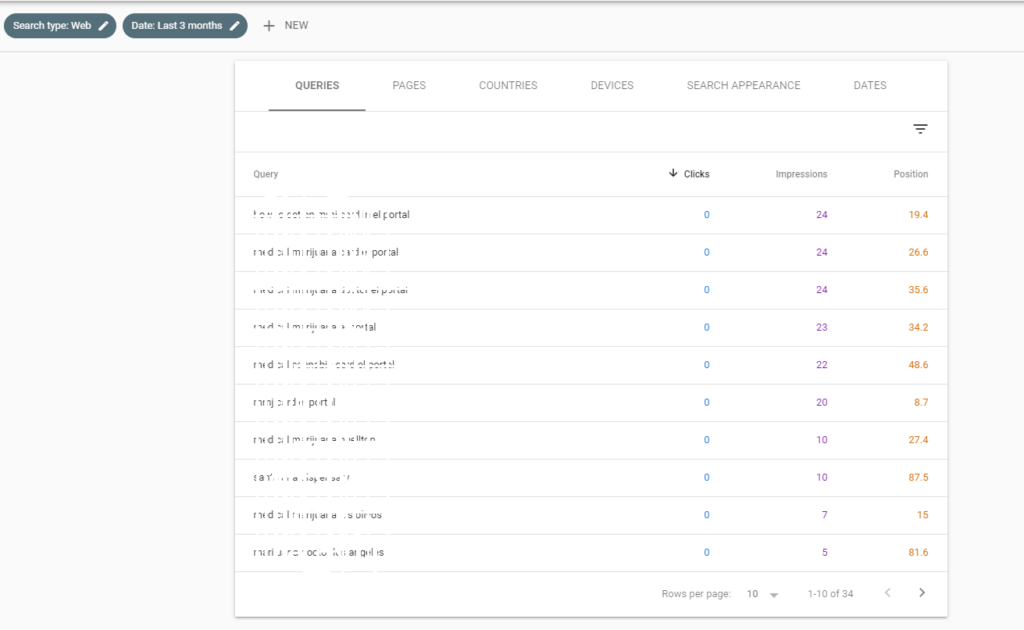
You can then refine this status quo as desired and filter it, for example, by country, device category (desktop, tablet & mobile) or the period (up to 16 months back). If your target market is Canada, for example, it is definitely advisable to filter this under "countries". I would like to introduce a few more interesting filters to common questions below.
How often is my brand searched for?
You would like to know how high the exact search volume of your brand is on Google? No problem: If you are already in the performance report, simply click on "NEW" and "Search query ...". Now enter your brand under "Exact request".
In this way, you will see a report for your brand keyword and can also select the time frame for which you need to see the data.
The impressions selection corresponds to the search volume in the selected period - because the impressions indicate how often one of your pages for the searched keyword appeared in Google's search results when someone entered the keyword that you viewing data of.
How often is it searched for terms without my brand name?
The so-called "generic keywords" for which your website was found in the search results can also be found easily in the Search Console. To do this, you must select "Search query ..." under "NEW" in the performance report and then filter and apply your brand name for "Search queries without".
Now you get an overview of the most impressive search queries without the brand - in our example "barfinfo":

This allows you to find out which generic search terms your website receives impressions and clicks. Especially when the position is on page 2, it is worth taking a closer look to find (unused) potential! Because you can find out different threshold keywords.
What types of searches can I evaluate in the Search Console?
In principle, you can choose between normal web search (default), image search, video search, and, more recently, news search. Google Webmaster announced the filtering for "News" on Twitter on July 21, 2020, and put it live.

So you can directly evaluate the performance of your content in the News tab of Google Search:

What is my page ranked for?
To find out for which keywords a specific page is ranked, simply enter the desired URL under "NEW", "Page ..." and "Exact URL". Please note that the entire URL really has to be copied in here and not the relative path without domain:

The Search Console then shows you all the search queries for which the specified URL is ranked:

But be careful: The Google Search Console only shows you results for those search queries that are being searched. Especially in the longtail area or if you are still very far behind, there are often few impressions and the graph then often gives the wrong impression:

If you have different directories on your website, you can also wonderfully evaluate their search performance in the GSC. Simply click on "NEW" again, select "Page ..." and select "URLs with" and insert the desired path:

Then you get an overview of URLs that have the path "/ barf-speiseplan /" and can then use it again as a filter and look at the search queries:
Do my landing pages compete internally for keywords?
It is important that your pages do not get in the way of the search queries for which they are to be found in the search engines. No keyword should be focused on more than one of your pages. If this is the case, we speak of keyword cannibalism. In this way, the sides harm each other, and both rank worse than they would without the other. You can find out whether keyword cannibalism occurs on your domain with special search queries via the performance report. Simply click on the desired keyword or search for it using "NEW" and "Search query ...".
Select the KPIs clicks, impressions and position to get an idea of the possible competition. The fact that several pages appeared under the same keyword in the search results in the last 12 months does not mean that this is keyword cannibalism. Only if there is no clear prioritization of the pages by Google and the pages have approximately the same number of impressions, you need to take measures:
The number of clicks, impressions and the average position shows such a large difference that we cannot speak of keyword cannibalism.
Here we see how two pages cannibalize for a selected keyword. You’ll get pretty high impressions and clicks. Here we recommend checking to what extent the keyword focus of a page can be changed so that Google only provides one page for keyword X.
If you want to examine two of your pages, which are quite similar in terms of content, with regard to keyword competition, you can also approach this topic from the landing page level. Select "NEW", "Page ..." and "Compare":

After you have entered the URLs to be examined, the Search Console shows you all the keywords, including the KPIs you have selected, for which the two sides rank. Unfortunately, the representation in the GSC is in need of optimization and not very clear, but you can easily export the data (as a CSV file or Google spreadsheet).
The presentation of the comparison option leaves something to be desired - only one of the selected KPIs can be compared while the search queries are displayed at the same time. However, this is bearable because you can simply download the data and view it in Excel.
If you use SEO Tools for Excel, you can export the data for a certain period of time as well as the keyword and the ranking URL. The great thing about it: You can easily find out multiple rankings by creating a pivot table.

In order to prevent keyword cannibalism and to keep an overview of the assignment of keywords and landing pages, I recommend that you create and maintain a keyword map for your domain.
How do I see how the rankings developed compared to the previous year?
If you want to know how your website performs compared to last year in relation to the KPIs of the GSC, you can also find out easily. Simply click on "Date: Last 3 months" (which is selected by default) and then switch to "COMPARE". Under "User-defined" you can then select the desired comparison period (note: the data "only" go back to 16 months so that you can compare a maximum of four months with the previous year period.

You can then look at the KPIs you want:

Of course, you can tailor the evaluation again and restrict it to a specific page or a specific page area, for example. The result looks something like this:
How can I find threshold keywords?
Threshold keywords are search queries that are on the threshold of a very good ranking. With them, you can achieve success very quickly. You can basically define these thresholds at which the search queries are located. The most common are search queries for which your pages rank on the border to Google's next results page (i.e. positions 11, 12). Another threshold to consider is the top 5 search results. Of course, it is also extremely worthwhile to move from position 2 to position 1. A targeted snippet optimization, a textual revision, or an intensified internal linking of the pages ranked here can already result in a significant increase in traffic.
To identify these searches, click "Search Queries". Make sure that you (a) choose the average positioning, (b) keep the time period up to date ("last 28 days"). You can now sort by positions and see directly which of your keywords rank on so-called thresholds:

You can be even more targeted by filtering for specific positions. In this way, however, you do not see all threshold keywords, you have to filter each position individually.
However, it is nicer if you create a list of all your threshold keywords. The best way to do this is to export the keywords for which your domain is ranked as a CSV file. After you have prepared the CSV data so that it can be read out in Excel, add another column called "Threshold Keyword" and set a filter. Now mark all relevant positions as threshold keywords and filter out all others:
These supposed threshold keywords need to be investigated further because the average position results from all positions of all of your pages that may rank for the search query.
Next, you only need to arrange the pages that rank for the search queries and decide where you want to screw (snippet, text, links, possibly technical troubleshooting) to push your ranking.
Here you have to pay attention to the following: You should always assume that several pages rank for the same keyword and thus falsify the average position displayed. So maybe it is just a threshold keyword at first glance. For example, if URL 1 (with 58 impressions in the last 7 days) for "swimming trunks" ranks 9th on average, while URL 2 (with 3 impressions in the same period) is on average in position 38, irrelevant URL 2 falsifies you Your result: In this case, the average position for "swimming trunks" is shown to 10.6, which corresponds to a threshold keyword. The relevant page - the only one that counts - is ranked on the 9th
How do I get a new page into the Google index as quickly as possible?
You have made changes to one of your pages and want Google to crawl this page again today rather than tomorrow? No problem. Simply enter the desired URL in the search field of the URL check and request re-indexing:

In this way you send Google the signal "Please take a look at this page again, I have changed it." Another tip: If it is a matter of rectifying technical errors, first use the live test of the URL check and request it new crawl when it shows that the topic has been resolved.
Does Google accept my canonical references?
In order to prevent duplicate content, a canonical reference is worthwhile in special cases in which 301 redirection is not useful. This reference tells Google that a page (to which Canonical refers) has similar or even identical content. The second info you send to Google is your prioritization. The canonical URL is the one you prefer, which you want to see in the search results (in contrast to the one referring to the canonical URL). So you tell Google which of the two pages you prefer and would like to have listed in the search results. The page that is not to be indexed can therefore no longer be reached via Google, but still via internal links on the domain - provided that Google acts as requested. It happens that Google does not accept these instructions: for example when used in combination with hreflang (an instruction for different country and language versions of the same content). If the hreflang attribute and the canonical reference contradict each other - for example, if a page is distinguished by hreflang as a German-speaking page for Switzerland, but canonically refers to the page relevant to Germany - this usually leads to Google ignoring your instructions and wants to find out how to deal with this topic.
In the URL check of the new Search Console, you can now check whether Google accepts your canonicals. Type the URL to be examined into the search field and see for yourself.
In this case, the URL points to another (the canonical) via Canonical - Google is accord.
Are there any soft 404 errors on my page?
Pages that have no (more) content should output a status code 404 (not found) or 410 (gone). If the status code 200 (ok) is sent instead, this is called a soft 404 error. The page looks like a 404 page but sends a conflicting response code.
You should definitely avoid these errors. If a large part of the crawl budget made available for your domain comes to nothing, it could be that your really relevant pages fall by the wayside. Search engines would also like to have their crawl budget used sensibly. If you let them crawl for free, they could be offended and cut your budget. Pages with little content ( thin content ) are sometimes handled as 404 pages and interpreted accordingly as Soft 404s. If the Search Console shows you such URLs as a soft 404 error, you should definitely react. The deletion of thin content affects very positively in general.
In the Search Console you will find Soft 404er in the index cover under the "Errors" tab:

The various types of errors found in your domain are listed here. Just click on "Submitted URL is a soft 404 error". If the number of different types of errors is so high that you cannot find the specific one you are looking for, you can (a) filter by error type and (b) contact us at any time ?

The URL check mentioned above is a great feature that gives you detailed information about the URLs of your choice. The live test is a useful debugging tool: it lets you immediately check whether the measures you took to fix a technical error were successful. If so, then it is advisable to request a new crawl from the affected page.

How can I integrate the GSC and what are the requirements for it?
The basic requirement for this is that you have a Google account, a website, and have access to the back end of this page or someone who manages it for you. Because a link to the website and the GSC is essential. Then simply go to the Google Search Console website, log in, and follow the next steps. How you create a property in the GSC, Google gives you information here. Depending on the selection of the GSC property type, there are various options for confirming the properties. If the GSC property is successfully confirmed, you will see the first data flutter in the next few days.
What are impressions, clicks, CTR, and average position on Google?
The four KPIs are the basis for the search analysis in the Google Search Console. If you click on the small question mark for each area, you will get information about the calculation:

Briefly described:
- The impressions indicate how often a URL of your website was seen in the Google search results for a selected search term. Since you will appear for every search query for your brand name, the number also corresponds to the search volume in the selected period.
- The clicks then show how often the respective keyword was finally clicked on.
- The CTR, i.e. click-through rate, is then calculated from the values of the impressions and clicks. The calculation looks like this:
(number of clicks/number of impressions) x 100. Example: If you are shown 100 times and clicked 1 time for the keyword “hiking”, the result is a CTR of 1%. - The average position is calculated as follows: (Highest position per day/day in a certain period.
Why can't I find my website on Google?
The basic question that arises here is: Is your website not found in the top positions for a certain keyword or is your website not at all in the search results because it may not (yet) be found in the Google index? In principle, you can use the so-called "site command" to check whether your domain can even be found in the index: "Site: [domain.de]" - you can also do the same at the URL level with "Site: [URL]" carry out.

Here you can check whether your page is just not ranked well or is still missing in the index. The latter can happen, for example, if your page is completely new or the domain has moved. Then you can easily speed up the indexing in the GSC. If your target URL is indexed, but it is not yet found well, you need to optimize it. You can find out whether you are found for a certain keyword by entering the keyword in "Search query". There are also various other keyword monitoring tools. If you need help improving your keyword rankings, feel free to contact us.
How often does Google crawl my page?
In the "Previous tools and reports" section, you can get an overview of your website's crawl statistics. Here you can see the Googlebot activities of the last 90 days. 
If you notice any anomalies here, you can carry out a log file analysis and check which pages have been crawled more often and can counteract them accordingly.
How can I delete URLs from the Google index?
In the "Index" and "Remove" reports, individual URLs, entire directories and domains can be removed from the index. This is usually done within a few hours. If you have incorrectly made distances here, you can also undo them. As a rule, the removed URLs are then pretty quickly back in the index - usually faster than if you removed URLs. 
How can I check my backlinks?
The "Links" report gives you an overview of external links with the most linked pages, the top-referring websites and the top-referencing text. You also get an overview of the most linked internal pages.
How do I find out if my website has undergone manual action?
Manual measures are activities on the part of Google if a webmaster has violated Google guidelines with his website. You can find out whether you are affected by this in the "Safety & Manual Measures" report. In this case, you would also receive a message that you can view under "Messages". Usually the result looks like this:
If not, you should act quickly. Google Webmasters offer Google Search Console training on YouTube, which deals with the topic of manual action. In this video, you will learn possible topics that lead to a manual measure as well as helpful information about steps that you should take if you are affected by a manual measure.
Can I speed up my domain change with the GSC?
If your website can be reached at a new address, you can actively inform Google in the Search Console. Under "Settings" and "Change of address" you then have the option to notify Google of the new GSC property for the existing GSC property. Important note: The new domain must be created as a property. The address change is only possible for domains - not for properties with URL directories.

What functions are available to me to optimize my site especially for mobile devices?
In principle, all reports are valid for this. Such as: With Search Performance, you can restrict by "Device". If you select "Mobile", this will then be a filter for the other data in the performance report. You can then use that to look at the mobile performance.  DON'T MISS ANY MORE POSTS: THE NEWSLETTER IN ONLINE MARKETING
DON'T MISS ANY MORE POSTS: THE NEWSLETTER IN ONLINE MARKETING
Do you like this blog post? If you want to keep up with the latest trends in online marketing, subscribe to our newsletter now. Over 13,000 subscribers trust us.
In addition, the report “User-friendliness on mobile devices” and the new “Core Web Vitals” are also particularly recommended, where, in addition to page speed, usability factors are also at stake.
I have awarded structured data. How do I see their performance and status quo?
A general overview of the performance of your built-in structured data is provided by the "Display in search" area. Here you can see how often results were displayed and ultimately clicked.

Tip: Click on the search results you want to evaluate and set a filter again. Then you can then look at the search queries and look at the exact performance and readjust if necessary.

The "Improvements" report shows whether your awards are correct or have errors, such as:

In the individual improvement areas you can see where there are errors, where there are pages with warnings and which URLs are valid. You should always take a closer look at the errors and warnings. Error messages in particular need to be implemented quickly. Warnings should also be checked and the feasibility for implementation evaluated.

How do I add other users in the GSC?
Under "Settings" and "Users & Permissions". But this only works if you are a confirmed owner. As a delegated owner (ownership has been granted by the verified owner), the "Users and Permissions" function is not available.
Where can I find help with further questions about the GSC?
- You can read everything about the Google Search Console on their website Search Console help
- Also recommended: Google Search Console Training on YouTube
- If you have further questions to which you have not yet found an answer, Google offers you with the Search Console help forum
Do you have any further questions about the Google Search Console or can you give yourself a tip for use? Then always with it ?